Why house dust mites (HDM) cause allergy
The reason why so many people are allergic to house dust mites is now clear. One of the mite's major allergens (found it its droppings) is an aggressive digestive enzyme that can attack and melt the 'glue' that binds delicate cells together. These cells are in the nose, lungs, eyes or on vulnerable skin. The mite's enzyme is so powerful that it can actually kill cells causing a breach in the body's defences. In mite sensitive people the enzyme's attack results in an immune reaction that is so fierce it can damage adjacent healthy cells causing a chain reaction of harm known as an allergic reaction. This is how house dust mites can cause allergy.
Mites are ancient animals that evolved about 600 million years ago, consequently many of the products that come from mites are completely foreign to man. When people are first exposed to house dust mite products their immune system can react in one of three ways: (1) It can ignore the mite as background dust, (2) note it as interesting (sensitised) and tolerate it, or, (3) become concerned and alert to its foreign presence. The last category can turn into an active allergy if the conditions are right. The conditions usually needed for this transformation are genetic influence, age, the amount of exposure, health, and life style. However, once an allergy to house dust mites is established, avoidance is required or the allergy can become worse.
The house dust mite (HDM)
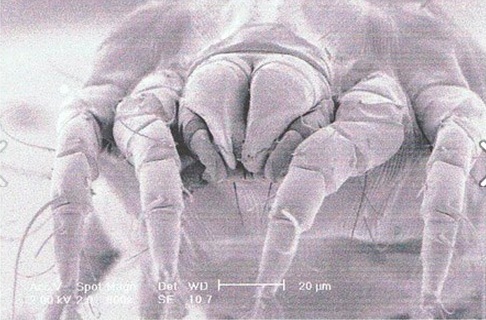
Kind permission of London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
In house dust mite droppings there are 14 fully identified separate proteins that have the potential to cause an allergy, but first they must enter the body to be noticed. This entrance can be achieved thanks to the active digestive enzyme mentioned above that can 'melt-the-glue' that holds cells together. The breach creates an important entrance for another major mite allergen, the 'con-artist', known scientifically as Der p2. This allergen can trick the immune system into believing it's been attacked by bacteria causing further alarm. Beware, an established allergy to house dust mites can confuse and overwhelm a vulnerable immune system causing allergic diseases such as asthma, rhinitis and allergic dermatitis, also known as eczema.
Children are said to be most at risk from allergy to house dust mites, because they may think it's normal to always wheeze, sneeze or itch.
'Allergens and their role in the allergic immune response', TAE Platts-Mills, JA Woodfolk 'Immunological Reviews', 2011 Vol. 242: 51-68
'Dangerous Allergens: Why Some Allergens are Bad Actors'. Steve N. Georas, Fariba Rezace, Laurie Learner' Lisa Beck, 'Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep'. 2010; 10: 92-98
'CpG Motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation'. Krieg, A.M. A.K. Yi, S. Matson, T.J. Waldschmidt, G.A. Bishop, R. Teasdale, G.A. Koretzky, and D.M. Klinman. 1995. 'Nature' (Lond.). 1995; 374: 546 - 549
'Is Permanent Parasitism Reversible? Critical Evidence from Early Evolution of House Dust Mites', Pavel B, Kilmov, Barry O'Connor, Oxford University Press Society of Systemic Biologists, Feb 13 2013

